Understanding Multiprocessor and Multicore Organization
Introduction
In modern computing, achieving higher performance and efficiency often involves using multiple processing units. Two primary ways to achieve this are through multiprocessor systems and multicore processors. This blog will explain these concepts, focusing on Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP) within multiprocessor systems and the organization of multicore processors.
Multiprocessor Systems
Multiprocessor systems involve using two or more separate CPUs (Central Processing Units) in a single computer system. These CPUs work together to perform tasks more efficiently. One common type of multiprocessor system is Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP).
Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP)
In SMP systems, all CPUs share the same memory and I/O (input/output) devices and run a single operating system. Here’s how it works:
- Shared Memory: All CPUs can access the same memory, which allows them to share data easily.
- Single OS: A single operating system manages all the CPUs, balancing the workload among them.
Benefits of SMP
- Performance: Multiple CPUs can work on different tasks simultaneously, increasing the overall speed of the system.
- Load Balancing: The operating system can distribute tasks evenly across all CPUs, preventing any single CPU from becoming a bottleneck.
- Fault Tolerance: If one CPU fails, the others can continue working, providing a level of reliability.
Applications of SMP
- Servers: Large servers that need to handle many requests at once often use SMP to ensure smooth and efficient operation.
- Workstations: High-end workstations used for tasks like video editing and 3D rendering can benefit from the increased performance of SMP.
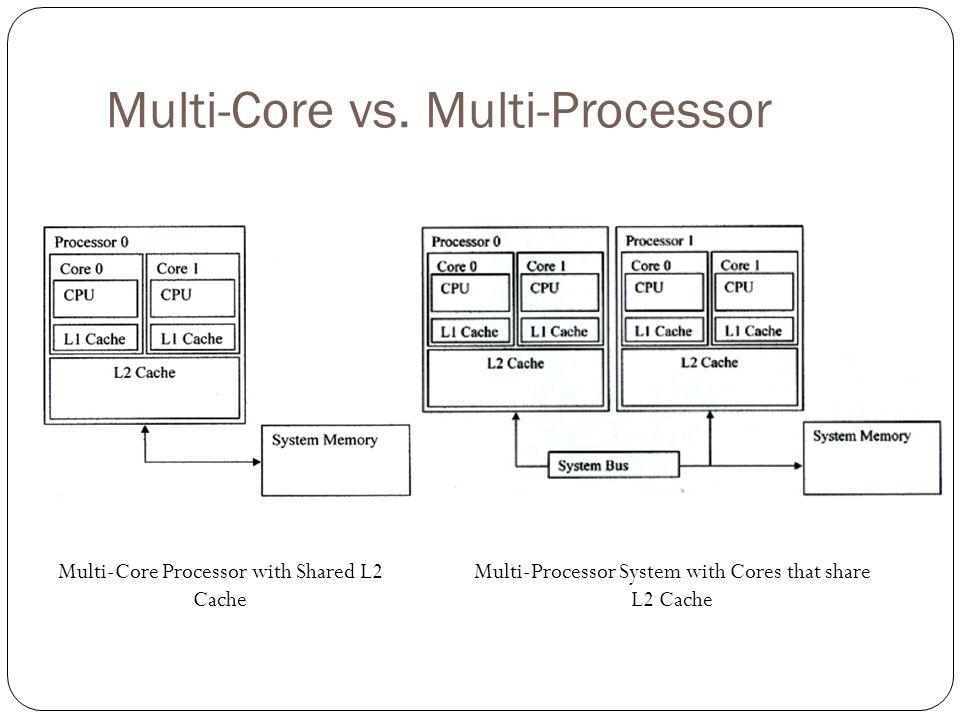
Multicore Processors
Multicore processors integrate multiple processing units, called cores, onto a single chip. Each core can execute its own instructions independently, allowing for parallel processing within a single processor package.
How Multicore Processors Work
- Multiple Cores: Each core can run its own thread, which means multiple threads can be executed simultaneously.
- Shared Resources: Cores may share certain resources like cache memory, which helps them communicate and work together efficiently.
Benefits of Multicore Processors
- Performance: Like multiprocessor systems, multicore processors can handle multiple tasks at once, increasing overall performance.
- Energy Efficiency: Multiple cores on a single chip use less power than multiple separate CPUs.
- Space Efficiency: Multicore processors take up less physical space than multiple single-core processors.
Applications of Multicore Processors
- Personal Computers: Most modern laptops and desktops use multicore processors to run applications faster and more efficiently.
- Mobile Devices: Smartphones and tablets use multicore processors to handle complex applications and multitasking.
- Gaming Consoles: Gaming systems use multicore processors to manage graphics and game physics smoothly.
Key Differences
- Structure: Multiprocessor systems have multiple separate CPUs, while multicore processors have multiple cores on a single chip.
- Usage: Multiprocessor systems are often used in high-performance and specialized applications, while multicore processors are common in everyday devices.
Conclusion
Both multiprocessor systems and multicore processors enhance computing performance by enabling parallel processing. SMP systems use multiple CPUs to share the workload and improve reliability, while multicore processors pack multiple cores into a single chip for efficient, high-performance computing in everyday devices. Understanding these concepts helps us appreciate the advanced technology behind the powerful devices we use daily.