


In operating systems, thread concurrency deals with the simultaneous execution of multiple threads, which can lead to issues like race conditions, where the outcome depends on the sequence or timing of the threads' execution. Two key concepts to manage these issues are mutual exclusion and synchronization.
Mutual Exclusion
Mutual exclusion ensures that when one thread is accessing a critical section of code (a part of the code that accesses shared resources), no other thread can enter that critical section until the first thread exits it. This prevents race conditions and ensures data consistency.
Mechanisms for Mutual Exclusion:
1. Locks (Mutexes): A lock is a synchronization primitive that provides mutual exclusion. When a thread locks a mutex, other threads attempting to lock it will block until the mutex is unlocked.
2. Spinlocks: Similar to mutexes, but a thread attempting to acquire a spinlock will continuously check and wait (spin) until the lock becomes available.
3. Semaphores: A semaphore can be used to control access to a resource by multiple threads. A binary semaphore (similar to a mutex) can ensure mutual exclusion.
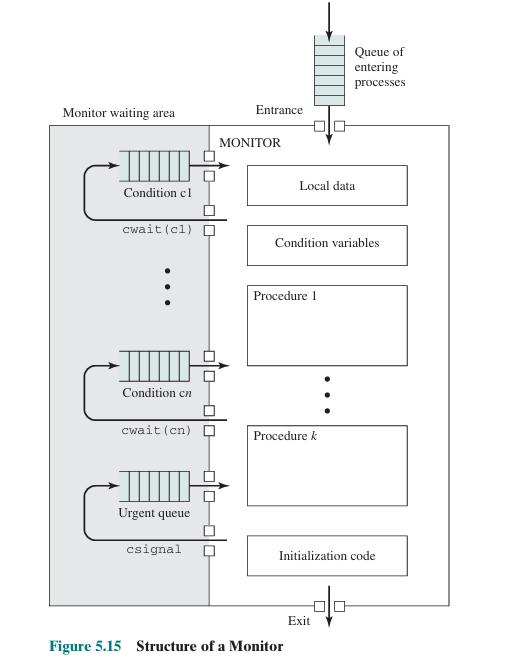
4. Monitors: A higher-level construct that combines mutual exclusion and synchronization by allowing only one thread to execute within the monitor at a time.
Synchronization
Synchronization ensures that threads coordinate their actions to achieve correct execution order. It involves controlling the sequence of thread execution and ensuring that threads wait for certain conditions to be met before proceeding.
Mechanisms for Synchronization:
1. Condition Variables: Used with mutexes to allow threads to wait for certain conditions to be met. A thread can wait on a condition variable, releasing the associated mutex, and another thread can signal the condition variable to wake up the waiting thread.
2. Semaphores: Besides mutual exclusion, semaphores can also be used for synchronization by signaling between threads.
3. Barriers: Synchronization primitive that enables multiple threads to wait until all threads have reached a certain point of execution before any of them proceed.
4. Event Objects: Used in some operating systems for threads to signal and wait for events.
Example Scenario
Consider a shared buffer that multiple producer threads write to and multiple consumer threads read from:
- Mutual Exclusion: A mutex can ensure that only one thread modifies the buffer at a time, preventing data corruption.
- Synchronization: Condition variables can synchronize the producer and consumer threads. Producers wait if the buffer is full, and consumers wait if the buffer is empty.
By using mutual exclusion and synchronization mechanisms appropriately, operating systems can manage thread concurrency, ensuring data integrity and correct execution order in multi-threaded applications.