


What is Deadlock?
Deadlock is a situation in computing where two or more processes are unable to proceed because each is waiting for the other to release resources.
Disadvantages of Deadlock:
Deadlock is an infinite process it means that once a process goes into deadlock it will never come out of the loop and the process will enter for an indefinite amount of time. There are only detection, resolution, and prevention techniques. But, there are no Deadlock-stopping techniques.
How Deadlock can occur?
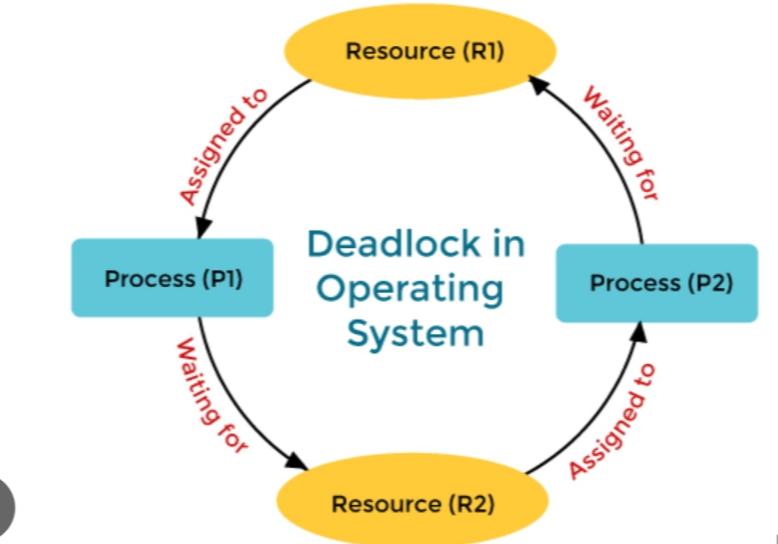
Lets consider following situation:
Process 1 requires Resource 2 to continue execution but is unable to do so because Process 2 is currently holding Resource 2. Similarly, Process 2 requires Resource 1 to continue execution but is unable to do so because Process 1 is currently holding Resource 1. Both processes are now stuck in a loop:
We have a deadlock because neither process can release the resource it is holding until it completes its task, and neither can proceed without the resource the other process is holding. Both processes are effectively “deadlocked,” unable to move forward. To break the deadlock and free up resources for other processes in this situation, an external intervention, such as the operating system killing one or both processes, would be required.
Necessary conditions for the occurrence of deadlock:
1) Mutual Exclusion:
Mutual Exclusion condition requires that at least one resource be held in a non-shareable mode, which means that only one process can use the resource at any given time.
As an example:
2) Hold and Wait:
The hold and wait condition specifies that a process must be holding at least one resource while waiting for other processes to release resources that are currently held by other processes. In our example,
3) No Preemption:
Preemption is the act of taking a resource from a process before it has finished its task. According to the no preemption condition, resources cannot be taken forcibly from a process a process can only release resources voluntarily after completing its task.
For example – Process1 have resource1 and requesting for resource2 that is hold by process2. then process1 preempt resource1 and after some time it try to restart by requesting both resource1 and resource2.
4) Circular Wait:
This condition implies that circular processes must exist, with each process waiting for a resource held by the next process in the chain. In our scenario, Process 1 is waiting for Resource 2, which is being held by Process 2. Process 2 is awaiting Resource 1 from Process 1. This circular chain of dependencies causes a deadlock because neither process can proceed, resulting in a system shutdown.
Conclusion:
Deadlocks are major problems in computers in which two or more processes remain blocked forever, each waiting for the other to release resources. A deadlock requires four conditions: mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. Deadlocks consume resources and reduce system performance, hence their avoidance, detection, and resolution are critical in operating systems.