



Introduction:
Session hijacking is a technique used by hackers to gain access to a target’s computer or online accounts. In a session hijacking attack, a hacker takes control of a user’s browsing session to gain access to their personal information and passwords.
Types:
1) Session Sniffing:
A sniffing attack occurs when an attacker uses a packet sniffer to intercept and read sensitive data passing through a network. Common targets for these attacks include unencrypted email messages, login credentials, and financial information.
Consequences of Session Sniffing:
A successful sniffing attack can have several severe consequences for the targets. These can include:
2) Cross-Site Scripting(XSS):
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is an attack in which an attacker injects malicious executable scripts into the code of a trusted application or website. Attackers often initiate an XSS attack by sending a malicious link to a user and enticing the user to click it. If the app or website lacks proper data sanitization, the malicious link executes the attacker’s chosen code on the user’s system. As a result, the attacker can steal the user’s active session cookie.
Cross-site scripting works by manipulating a vulnerable web site so that it returns malicious JavaScript to users. When the malicious code executes inside a victim's browser, the attacker can fully compromise their interaction with the application.
3) Cross-Site Request Forgery(CSRF):
Cross-site request forgery (also known as CSRF) is a web security vulnerability that allows an attacker to induce users to perform actions that they do not intend to perform. It allows an attacker to partly circumvent the same origin policy, which is designed to prevent different websites from interfering with each other.
In a successful CSRF attack, the attacker causes the victim user to carry out an action unintentionally. For example, this might be to change the email address on their account, to change their password, or to make a funds transfer. Depending on the nature of the action, the attacker might be able to gain full control over the user's account. If the compromised user has a privileged role within the application, then the attacker might be able to take full control of all the application's data and functionality.
4) Brute Force Attack:
A brute force attack is a hacking method that uses trial and error to crack passwords, login credentials, and encryption keys. It is a simple yet reliable tactic for gaining unauthorized access to individual accounts and organizations’ systems and networks. The hacker tries multiple usernames and passwords, often using a computer to test a wide range of combinations, until they find the correct login information.
The name "brute force" comes from attackers using excessively forceful attempts to gain access to user accounts. Despite being an old cyberattack method, brute force attacks are tried and tested and remain a popular tactic with hackers.
Here’s how hackers benefit from brute force attacks:
5) Session Fixation:
A Session fixation attack is an attack that occurs when a malicious user sets up a fake session before the legitimate users are able to log in. This leads to the entire system getting compromised and used to steal sensitive data.
Anatomy of a Session Fixation Attack:
A typical session fixation attack is performed as follows:
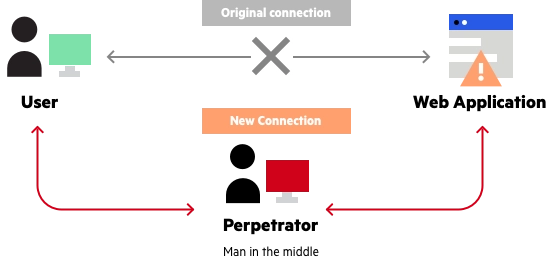
6) Man-in-the-Middle Attack(MITM):
A man in the middle (MITM) attack is a general term for when a perpetrator positions himself in a conversation between a user and an application—either to eavesdrop or to impersonate one of the parties, making it appear as if a normal exchange of information is underway.
The goal of an attack is to steal personal information, such as login credentials, account details and credit card numbers. Targets are typically the users of financial applications, SaaS businesses, e-commerce sites and other websites where logging in is required.
Information obtained during an attack could be used for many purposes, including identity theft, unapproved fund transfers or an illicit password change.
Additionally, it can be used to gain a foothold inside a secured perimeter during the infiltration stage of an advanced persistent threat (APT) assault.
Broadly speaking, a MITM attack is the equivalent of a mailman opening your bank statement, writing down your account details and then resealing the envelope and delivering it to your door.
Prevention of Session Hijacking Techniques:
There are several ways to prevent session hijacking from happening:
Conclusion:
Session hijacking can have several dangerous consequences. The most dangerous consequence of session hijacking is that the malicious attacker can gain entry to the server and access its data without first hacking a valid account.