


In operating systems, threads are lightweight units of execution that enable concurrent execution of multiple tasks within a single process. Threads are also known as lightweight processes as they share the same resources, such as memory and files, with other threads within the process.
In operating systems, threads are lightweight units of execution that enable a program to perform multiple tasks concurrently. They are like independent streams of instructions within a single process. Threads provide a way to achieve parallelism, allowing different parts of a program to execute simultaneously, enhancing performance and responsiveness. Let's explore the different types of threads in simple terms:
1. User-level Threads (ULTs):
User-level threads are managed entirely by the application or program without the involvement of the operating system. The thread management library within the application handles thread creation, scheduling, and synchronization. ULTs are lightweight and fast to create and switch between, but they can't take advantage of multiple processor cores directly. If a user-level thread blocks or performs a lengthy operation, it can impact the responsiveness of other threads in the same process.
2. Kernel-level Threads (KLTs):
Kernel-level threads are managed by the operating system kernel. The kernel allocates a separate thread control block for each thread, allowing it to schedule threads across multiple processes. KLTs can run in parallel on multiple processor cores, leveraging the benefits of multiprocessing. Context switches between kernel-level threads involve higher overhead compared to ULTs.
3. Hybrid Threads:
Hybrid threads aim to combine the advantages of ULTs and KLTs. In this approach, multiple user-level threads are associated with a smaller number of kernel-level threads. The operating system schedules the kernel-level threads, while the user-level threads are managed by the application. This hybrid model provides a balance between fine-grained control and efficient use of system resources.
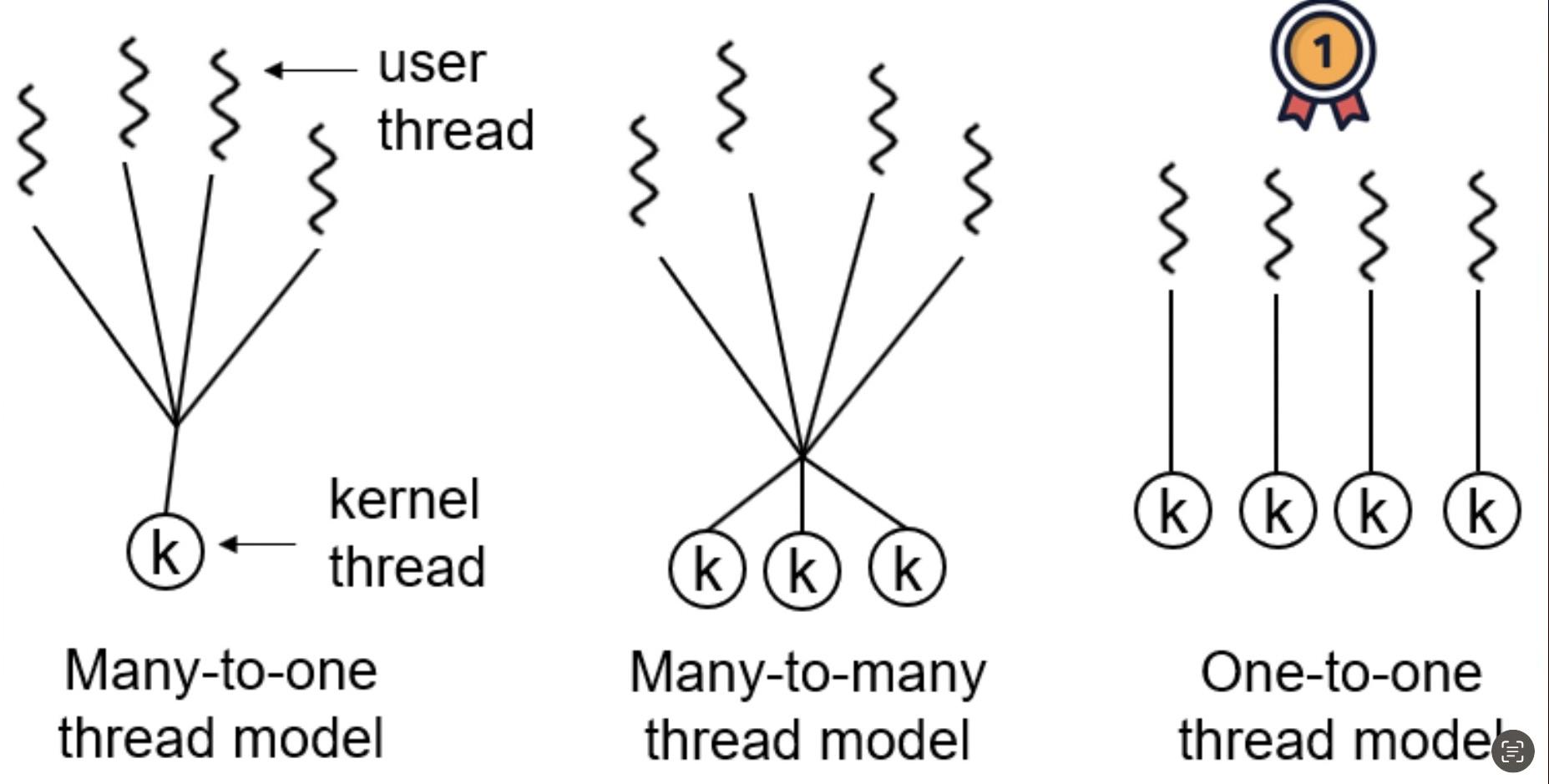
4. Many-to-One (M:1) Model:
The M:1 threading model maps many user-level threads to a single kernel-level thread. This model relies on the thread library in the application to handle thread scheduling and synchronization. While it provides flexibility and efficiency for managing user-level threads, it can suffer from limited parallelism due to the dependency on a single kernel-level thread.
5. One-to-One (1:1) Model:
The 1:1 threading model maps each user-level thread to a corresponding kernel-level thread. This model offers better parallelism as each user-level thread can run on a separate processor core. However, creating and managing a large number of kernel-level threads can introduce overhead.
6. Many-to-Many (M:N) Model:
The M:N threading model is a combination of the M:1 and 1:1 models. It allows multiple user-level threads to be mapped to a smaller or equal number of kernel-level threads. This model provides flexibility and allows efficient use of system resources. However, it requires coordination between the user-level thread library and the kernel for effective scheduling.
In summary, threads in operating systems can be categorized into user-level threads, kernel-level threads, and hybrid threads. Different threading models, such as M:1, 1:1, and M:N, determine the relationship between user-level and kernel-level threads and influence their management and parallelism capabilities.