


Advantages:
1. Quick Response: Threads keep apps alert to user actions or outside events while doing other jobs in the background. A web browser handles clicks and downloads files at the same time.
2. Shared Tools: Threads in one process can use the same tools like memory and file access. This makes sharing data easier than between processes, which need complex ways to talk to each other.
3. Better Use: Threads make the most of computers with many cores. They run at the same time on different cores, which can speed up jobs that can be split up.
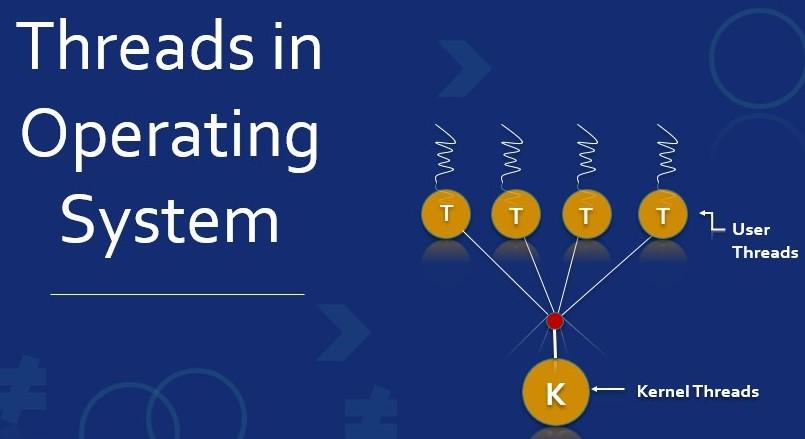
Types of Threads:
1. App-Level Threads: The app controls these without help from the core system. The computer sees the whole process as one thing. So if one thread gets stuck (like waiting for input), the whole process might stop.
2. Kernel-Level Threads: The operating system kernel backs and oversees these threads . The kernel views each thread as its own unit boosting parallel processing. These threads can deal with operations that pause . Kernel-level threads have an influence on how the system handles tasks that might slow things down.
Thread States:
Threads go through different phases as they run:
1. Running: The CPU executes the thread's instructions.
2. Ready: The thread waits for its turn on the CPU.
3. Blocked: An event, like an I/O operation, holds up the thread.
4. Terminated: The thread completes its job.
Thread Synchronization and Communication:
Threads must coordinate when they use shared stuff to avoid mess-ups and keep data accurate. Tools like mutexes, semaphores, and condition variables help threads work together and talk to each other.
Examples of Thread Usage:
1. Graphical User Interface (GUI): Threads handle clicks and show changes at the same time.
2. Web Servers: Threads take care of many users at once making servers work better and faster.
3. Parallel Computing: Tasks like data processing and scientific simulations gain advantages from threads. These threads split workloads across multiple cores.
To sum up, threads offer a robust tool for concurrent programming within a process. They boost app responsiveness, resource sharing, and performance on modern multi-core systems. Developers must grasp thread management and synchronization. This know-how proves vital for creating efficient scalable software in today's computing landscape.