


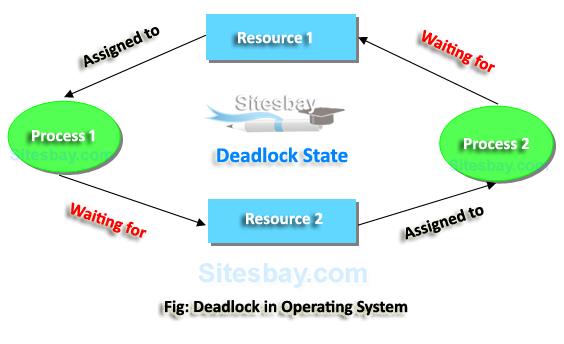
Deadlock in an operating system occurs when a set of processes become stuck in a situation where none of them can proceed because each process is waiting for a resource that another process holds. This creates a cycle of dependencies that prevents any of the involved processes from continuing.
### Necessary Conditions for Deadlock
For a deadlock to occur, four conditions must be present simultaneously:
1. **Mutual Exclusion**: At least one resource must be held in a non-shareable mode, meaning only one process can use the resource at any given time.
2. **Hold and Wait**: A process is holding at least one resource and is waiting to acquire additional resources that are currently being held by other processes.
3. **No Preemption**: Resources cannot be forcibly taken from a process. They can only be released voluntarily by the process holding them.
4. **Circular Wait**: There exists a set of processes \(\{P_1, P_2, \dots, P_n\}\) such that \(P_1\) is waiting for a resource held by \(P_2\), \(P_2\) is waiting for a resource held by \(P_3\), and so on, with \(P_n\) waiting for a resource held by \(P_1\).
### Deadlock Handling Methods
There are several strategies for handling deadlocks:
1. **Deadlock Prevention**: Modify the system design to ensure that at least one of the necessary conditions for deadlock cannot hold. This could involve:
- **Eliminating Mutual Exclusion**: Make resources sharable, if possible.
- **Eliminating Hold and Wait**: Require processes to request all required resources at once.
- **Eliminating No Preemption**: Allow the system to forcibly take resources from a process.
- **Eliminating Circular Wait**: Impose an order on resource acquisition.
2. **Deadlock Avoidance**: Dynamically examine the resource allocation state to ensure that a circular wait condition never occurs. The **Banker’s algorithm** is a classic example of a deadlock avoidance algorithm.
3. **Deadlock Detection and Recovery**: Allow deadlocks to occur but have the system detect them and take action to recover. Recovery can involve:
- **Terminating Processes**: Killing one or more processes to break the deadlock.
- **Resource Preemption**: Temporarily taking resources away from some processes and reallocating them.
4. **Ignoring Deadlock**: In some systems, deadlock is considered a rare event, so it's ignored. This approach is used by some operating systems like UNIX, where the system does nothing to prevent or avoid deadlock, relying instead on rebooting the system if a deadlock occurs.
Understanding deadlocks and how to handle them is crucial in the design and operation of reliable and efficient operating systems.