What is Starvation
Starvation is a problem with resource management where a process runs out of resources in the OS because those resources are being utilised by other processes. This issue primarily arises in a priority-based scheduling system where requests with high priority are processed first and those with low priority take longer to process.
What exactly does starvation mean in operating systems?
Problems arise when high-priority requests lead low-priority processes to become stalled for an extended period of time. The low-priority process cannot get the processor or resources because of a constant stream of high-priority demands. Starvation typically occurs when a task is postponed for an endless amount of time. The operating system requires the following resources to respond to process requests:
- I/O access to disk or network
- Memory
- Disk space
- Bandwidth of network
- CPU time
What Leads to Starvation?
Following are a few causes of OS starvation:
- If a higher priority operation uses a CPU continuously, a low priority process may wait indefinitely in starvation.
- Deadlock does not happen because low-priority processes do not interact with resources, but because they are stuck in a waiting state, there is a risk of starving.
- Thus, hunger is a fail-safe strategy, as it prevents deadlock temporarily but has an overall negative impact on the system.
- The main contributor to starving may be the fact that not enough resources are available to meet all needs.
- There is a chance that a process may have to wait for a long time if a process selection is random.
- Starvation can also happen when an improper resource allocation prevents a process from ever receiving a resource for use.
Various Approaches to Tackle Starvation
The following are some options for dealing with the starving condition in OS:
- To make sure that resources are distributed equally, a freelancing manager should be in charge of CPU resource allocation.
- Starvation happens as a result of random process method selection, which should be avoided.
- To prevent starvation, the ageing criterion for processes should be taken into account while allocating resources.
- To prevent starvation, a scheduling method with a priority queue can be utilised.
- If the random approach must be employed, treat starvation by combining it with a priority queue.
- The multilevel feedback queue can also be utilised to prevent operating system starvation.
Example:


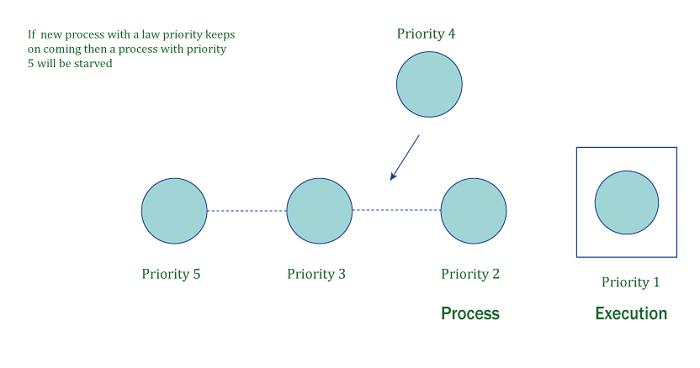
The P2 process is given the highest priority in the example, while P1 is given the lowest priority. There are n processes that are ready to be executed, as shown in the diagram. As a result, P2 will enter the CPU as the process with the greatest priority, while P1 will continue to wait for its turn because P1 is low on the priority list for all other processes. Starvation is the term used to describe the state in which the process is waiting.
- Causes of Starvation in OS:
- If a higher priority operation uses a CPU continuously, a low priority process may wait indefinitely in starvation.
- Resources are not available in sufficient quantities to meet all needs.
- There is a chance that a process may have to wait for a long time if a process selection is random.
- Due to improper resource allocation, a process is never given a resource to use for execution.
- Various OS Starvation Management Techniques
- To make sure that resources are distributed equally, a freelancing manager should be in charge of CPU resource allocation.
- It is best to avoid selecting a process approach at random.
- It is important to take processes' ageing requirements into account.
- There is a chance that a process may have to wait for a long time if a process selection is random.
- Starvation can also happen when an improper resource allocation prevents a process from ever receiving a resource for use.
Nikita Mitna
53003230109
Div-A