


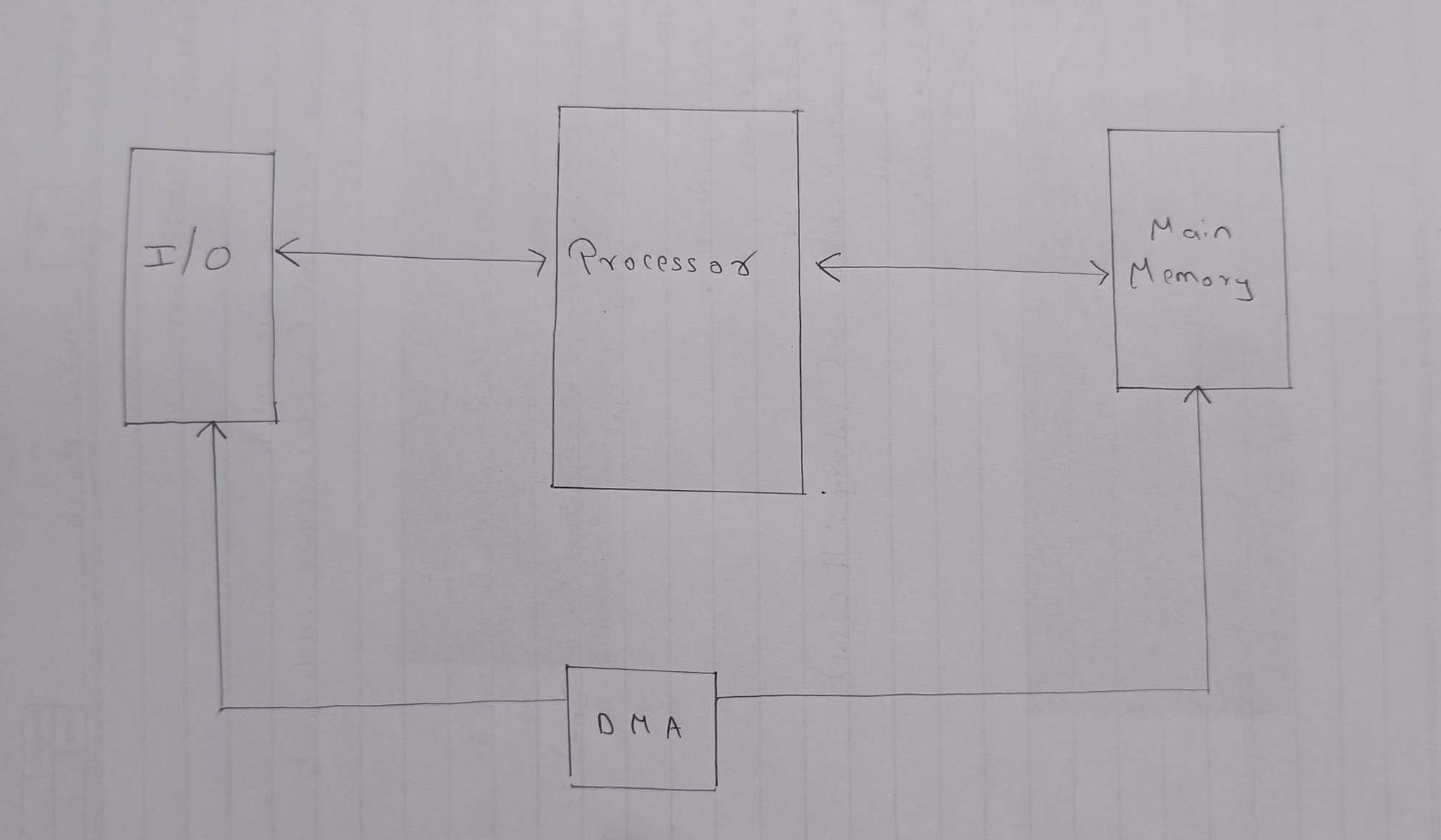
In the field of input/output (I/O) operations in computing systems, there are several methods to control the interface between the processor and peripheral devices. These methods—programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O, and direct memory access (DMA)—each have their own benefits and disadvantages.
Programmed I/O is the most basic method. In instances where the I/O module encounters an I/O instruction, the processor ends it through direct communication with it. The module performs the requested task and updated its status register but does not interrupt the processor. Instead, the processor must actively poll the module to check if the operation has finished. This polling can lead to significant performance degradation since the processor essentially waits idly during this period.
In the situation where the transfer of data of large volumes is involved, DMA is by far the best option.
DMA, the processor is allowed to pass off the transfer of data tasks to a specific DMA module.
Let’s dig into it a bit more if you don’t mind: The processor begins the transfer by giving the parameters such as the operation type (read-write), the device address, the memory location, and the data size to the DMA module. Once set up, the bus is taken over by the DMA module and memory is directly interfaced with the I/O devices without the processor involvement at each data word. This way significantly saves the processor's time and data is transferred much faster.
However, DMA may have some disadvantages. When the DMA module and the processor compete for bus access, there are situations when the processor may have to pause for a while to get the bus. This is a kind of intertemporal pause, and it takes place only on rare occasions due to DMA, which, by the way, remains much better as compared to programmed and interrupt-driven I/O methods in data handling.
As is clear from the above paragraph, among the three mentioned data transfer methods, the direct memory access (DMA) technique comes with the least workload to the CPU and hence is the most effective. By making memory to I/O transfers request in a very fast time, the DMA sends out information that the computer principle memory has been doing the same. This process makes the CPU to focus on other tasks than data transfer hence achieving high overall system efficiency.