


A buffer is a memory area that stores data being transferred between two devices or between a device and an application.
Buffering is done to deal effectively with a speed mismatch between the producer and consumer of the data stream.
A buffer is produced in main memory to heap up the bytes received from modem.
After receiving the data in the buffer, the data get transferred to disk from buffer in a single operation.
This process of data transfer is not instantaneous, therefore the modem needs another buffer in order to store additional incoming data.
When the first buffer got filled, then it is requested to transfer the data to disk.
The modem then starts filling the additional incoming data in the second buffer while the data in the first buffer getting transferred to disk.
When both the buffers completed their tasks, then the modem switches back to the first buffer while the data from the second buffer get transferred to the disk.
The use of two buffers disintegrates the producer and the consumer of the data, thus minimizes the time requirements
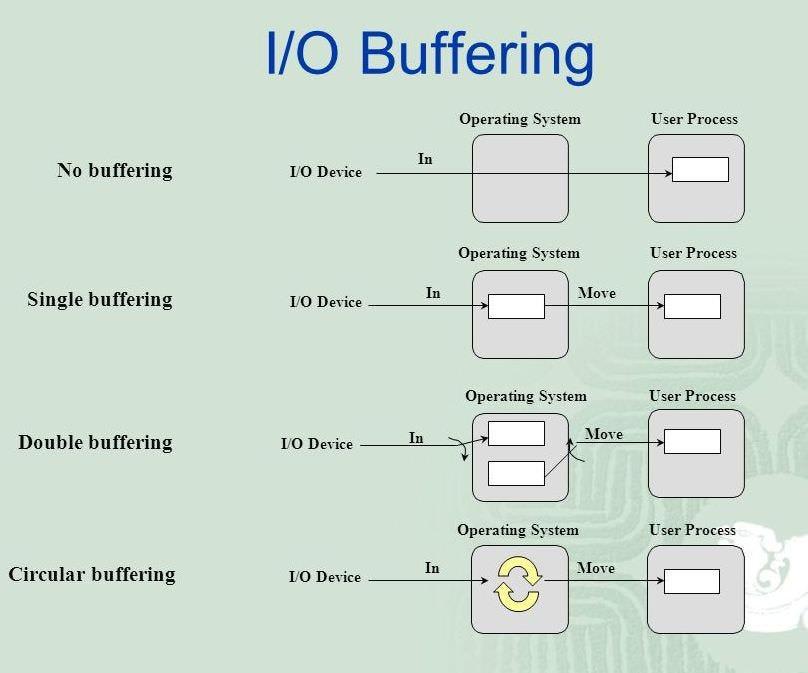
Types of various I/O buffering techniques :
A buffer is provided by the operating system to the system portion of the main memory.
Block oriented device –System buffer takes the input.
After taking the input, the block gets transferred to the user space by the process and then the process requests for another block.
Two blocks works simultaneously, when one block of data is processed by the user process, the next block is being read in.
OS can swap the processes.
OS can record the data of system buffer to user processes.
Stream oriented device –
Line- at a time operation is used for scroll made terminals. User inputs one line at a time, with a carriage return signaling at the end of a line.
Byte-at a time operation is used on forms mode, terminals when each keystroke is significant
Block oriented –There are two buffers in the system.
One buffer is used by the driver or controller to store data while waiting for it to be taken by higher level of the hierarchy.
Other buffer is used to store data from the lower level module.
Double buffering is also known as buffer swapping.
A major disadvantage of double buffering is that the complexity of the process get increased.
If the process performs rapid bursts of I/O, then using double buffering may be deficient.
Stream oriented –Line- at a time I/O, the user process need not be suspended for input or output, unless process runs ahead of the double buffer.
Byte- at a time operations, double buffer offers no advantage over a single buffer of twice the length.