


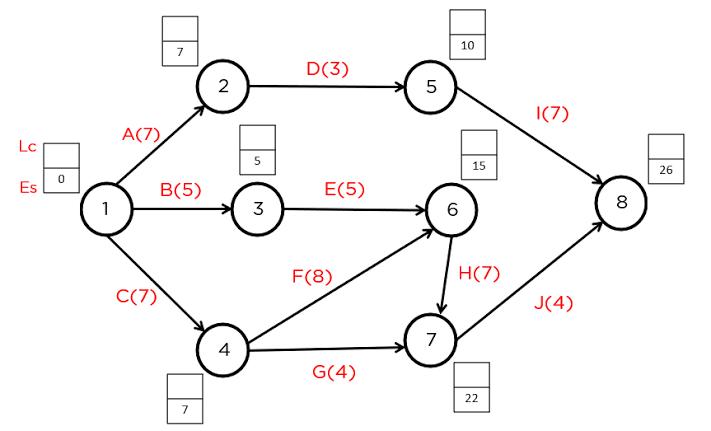
PERT event: a point that marks the start or completion of one or more activities. It consumes no time and uses no resources. When it marks the completion of one or more activities, it is not "reached" (does not occur) until all of the activities leading to that event have been completed.
predecessor event: an event that immediately precedes some other event without any other events intervening. An event can have multiple predecessor events and can be the predecessor of multiple events.
successor event: an event that immediately follows some other event without any other intervening events. An event can have multiple successor events and can be the successor of multiple events.
Besides events, PERT also knows activities and sub-activities:
PERT activity: the actual performance of a task which consumes time and requires resources (such as labor, materials, space, machinery). It can be understood as representing the time, effort, and resources required to move from one event to another. A PERT activity cannot be performed until the predecessor event has occurred.
PERT sub-activity: a PERT activity can be further decomposed into a set of sub-activities. For example, activity A1 can be decomposed into A1.1, A1.2 and A1.3. Sub-activities have all the properties of activities; in particular, a sub-activity has predecessor or successor events just like an activity. A sub-activity can be decomposed again into finer-grained sub-activities.
PERT has defined four types of time required to accomplish an activity:
optimistic time: the minimum possible time required to accomplish an activity (o) or a path (O), assuming everything proceeds better than is normally expected
pessimistic time: the maximum possible time required to accomplish an activity (p) or a path (P), assuming everything goes wrong (but excluding major catastrophes).
most likely time: the best estimate of the time required to accomplish an activity (m) or a path (M), assuming everything proceeds as normal.
expected time: the best estimate of the time required to accomplish an activity (te) or a path (TE), accounting for the fact that things don't always proceed as normal (the implication being that the expected time is the average time the task would require if the task were repeated on a number of occasions over an extended period of time).