


Processes in the context of computing refer to instances of executing programs on a computer system. Each process has its own memory space, resources, and execution context. Here's a breakdown of the key aspects related to processes:
Memory Space: Each process typically has its own memory space, which includes the executable code, variables, stacks, heaps, etc.
Resource Allocation: Processes may require various system resources (CPU time, memory, files) which are allocated to them by the operating system.
2.Process Control:
Scheduling: The operating system scheduler decides which process gets to use the CPU and for how long, based on scheduling algorithms (e.g., round-robin, priority-based scheduling).
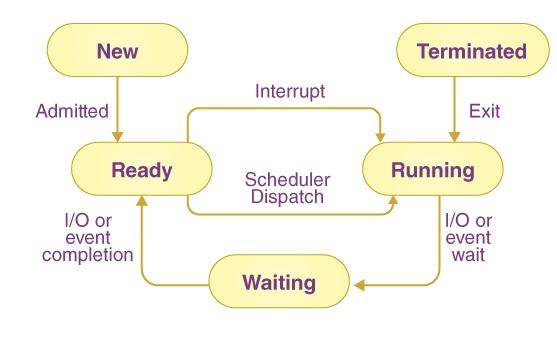
Execution State: Processes transition between different states such as running, ready, waiting (blocked), or terminated. State transitions are managed by the operating system scheduler and are influenced by events like I/O operations, timers, and signals.
3. Process Communication and Synchronization:
Mechanisms for inter-process communication (IPC) include shared memory, message passing (pipes, sockets, message queues), and synchronization primitives (mutexes, semaphores) to coordinate access to shared resources.
4.Process States:
Understanding processes and their control is fundamental to operating system design, resource management, and application development, especially in ensuring efficient and stable execution of programs on a computer system.