


Objectives of an Operating System
An operating system (OS) is essential software that manages a computer’s hardware and software resources. Here are its main objectives:
1.Resource Management: The OS manages the computer's hardware resources, including the CPU, memory, storage devices, and peripherals, ensuring they are used efficiently.
2.User Interface: The OS provides a user-friendly interface, either through a command-line interface (CLI) or a graphical user interface (GUI), making it easier for users to interact with the computer.
3.Application Execution: The OS loads and runs applications, managing multitasking to allow multiple programs to run simultaneously without conflicts.
4.File Management: The OS organizes and manages files on storage devices, handling the creation, deletion, reading, and writing of files.
5.Security and Access Control: The OS protects the system’s data and resources from unauthorized access, providing authentication and access control mechanisms.
6.Error Handling: The OS detects and handles errors to maintain system stability and prevent crashes.
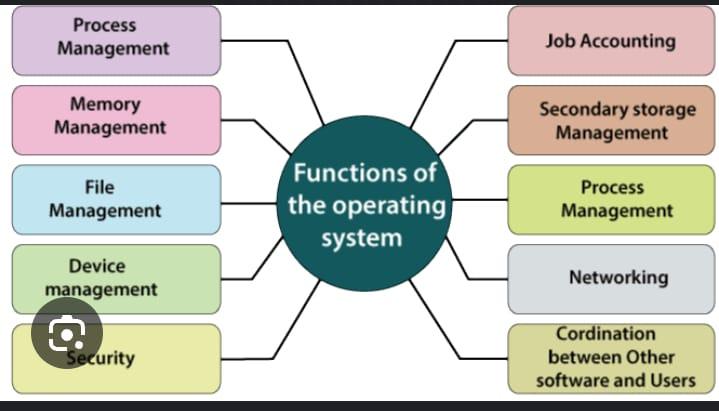
Functions of an Operating System
To achieve these objectives, an OS performs several key functions:
1.Process Management: The OS manages processes by scheduling them, allocating CPU time, and handling synchronization and communication between processes.
2.Memory Management: The OS allocates memory to processes, keeps track of free and used memory, and optimizes performance by managing data between physical memory and disk storage.
3.Storage Management: The OS manages data storage on devices like hard drives and SSDs, organizing files into directories and ensuring data integrity.
4.Device Management: The OS communicates with hardware devices through device drivers, translating OS commands into actions performed by the hardware.
5.User Management: The OS manages user accounts, permissions, and settings, ensuring users have appropriate access to system resources.
6.Networking: The OS enables networking capabilities, allowing computers to communicate over local networks and the internet, and handles data transmission and network protocols.