


1] Deadlock :
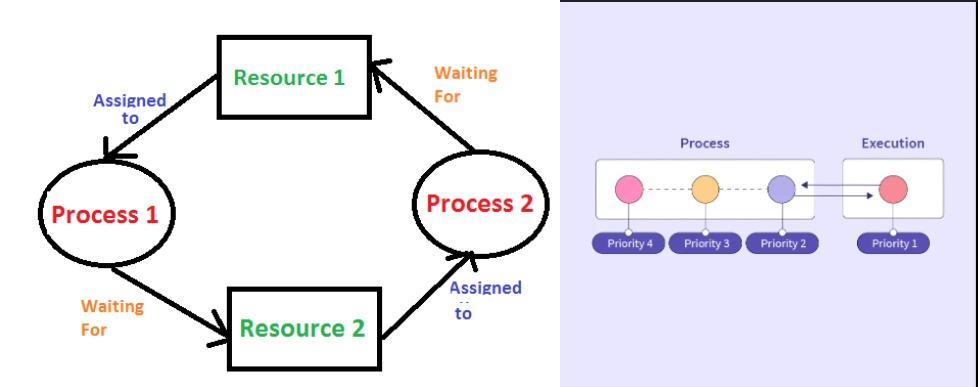
Deadlock is a situation where a set of processes becomes stuck, each waiting for a resource that the other processes in the set are holding. This results in a cycle of dependencies where no process can proceed, leading to a complete halt in the system. Deadlock typically occurs under four conditions, known as Coffman’s conditions:
1. Mutual Exclusion: At least one resource must be held in a non-shareable mode, meaning that only one process can use the resource at a time.
2. Hold and Wait: A process holding at least one resource is waiting to acquire additional resources that are currently being held by other processes.
3. No Preemption: A resource can be released only voluntarily by the process holding it after that process has completed its task.
4. Circular Wait: There must be a circular chain of processes, where each process holds at least one resource that the next process in the chain needs.
--Deadlock prevention, avoidance, detection, and recovery are the primary strategies used to handle deadlocks.
Prevention involves breaking one of Coffman’s conditions, whereas avoidance uses algorithms like the Banker’s Algorithm to ensure that the system remains in a safe state. Detection algorithms can identify deadlock when it occurs, and recovery techniques involve terminating or rolling back processes to break the deadlock.
2] Starvation :
Starvation, on the other hand, occurs when a process is perpetually denied the resources it needs to proceed. Unlike deadlock, where processes are waiting on each other in a cycle, starvation involves one or more processes being overlooked in favor of others. This often happens in scheduling algorithms that prioritize certain processes, causing lower-priority processes to wait indefinitely.
For example, in a priority-based scheduling system, a low-priority process might never get CPU time if higher-priority processes continuously arrive. Starvation is particularly problematic in systems where fairness and equitable resource allocation are critical.
To mitigate starvation, algorithms such as aging are used, where the priority of a process increases the longer it waits, eventually ensuring that it will receive the necessary resources.