Threads
A thread is a single sequential flow of activities being executed in a process it is also known as thread of execution or thread of control. There is a way of thread execution inside the process of any operating system. Thread is often referred to as a lightweight process. Threads aren’t actually allowed to exist outside the process. A single process can have several threads. Each thread has its own control block.
Need of Thread:
o It takes far less time to create a new thread in an existing process than to create a new process.
o Threads can share the common data; they do not need to use Inter- Process communication.
o Context switching is faster when working with threads.
o It takes less time to terminate a thread than a process.
o Threads enable parallel processing, increasing overall system performance and throughout.
o Threads are on the basis of real time system.
o Priority can be assigned to threads just like process, and the thread with highest priority is executed first.
Components of Threads:
Any thread has the following components.
1. Program counter
2. Register set
3. Stack space
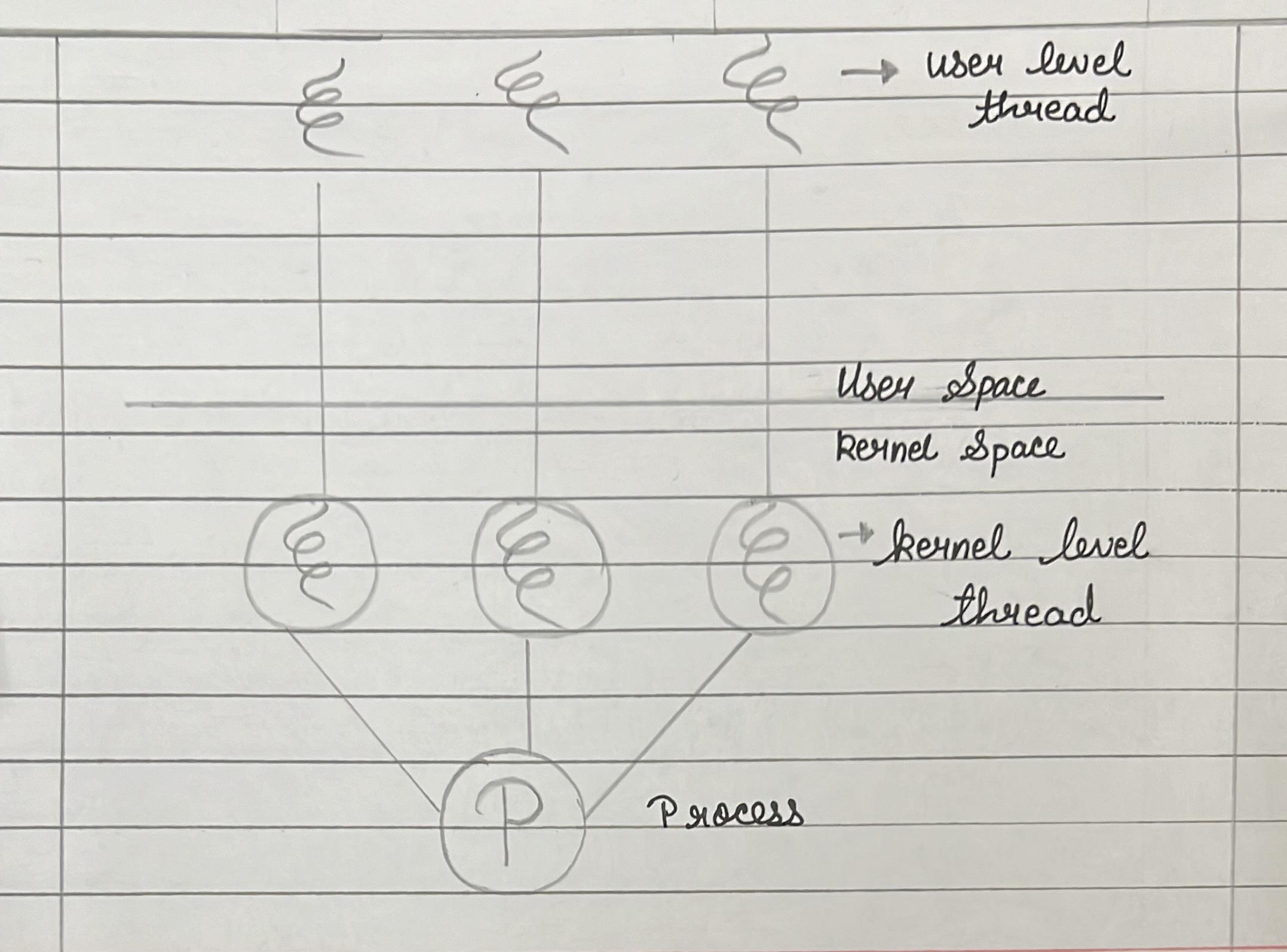
Types of Threads:
In the operating system, there are two types of threads.
1. Kernel level thread.
The operating system is recognized by the kernel thread. Each thread has a process in this level that has its own thread control block as well as control block system. The kernel is aware of all threads and it controls them. It provides a system call for the user space thread creation and management. For example: Solaris.
Advantages of Kernel-level threads
1. The kernel-level thread is fully aware of all threads.
2. The scheduler may decide to spend more CPU time in the process of threads being large numerical.
3. The kernel-level thread is good for those applications that block the frequency.
Disadvantages of Kernel-level threads
1. The kernel thread manages and schedules all threads.
2. The implementation of kernel threads is difficult than the user thread.
3. The kernel-level thread is slower than user-level threads.
2. User-level thread.
The user level thread is ignored by the operating system. This threads are simple to implement and are done so by the user. The entire process is blocked if a user executes a user level operation of thread blocking. For example: Java, POSIX.
Advantages of User-level threads
1. The user threads can be easily implemented than the kernel thread.
2. User-level threads can be applied to such types of operating systems that do not support threads at the kernel-level.
3. It is faster and efficient.
Disadvantages of User-level threads
1. User-level threads lack coordination between the thread and the kernel.
2. If a thread causes a page fault, the entire process is blocked.