



The Human Element in Cybersecurity: A Double-Edged Sword
Humans are an integral part of the digital landscape. From designing intricate security protocols to managing sensitive data, our involvement is inescapable. Yet, this very involvement becomes a double-edged sword when it comes to cybersecurity. While human ingenuity has led to incredible technological advancements, our fallibility can also open the door to malicious intent and unintended breaches.
Understanding Human Errors in Cybersecurity
Human errors in cybersecurity can take various forms, each with its own set of consequences:
Phishing Attacks: One of the most common forms of cyberattacks, phishing relies on manipulating individuals into revealing confidential information. A simple click on a seemingly harmless link or the download of a malicious attachment can expose an entire network to vulnerabilities.
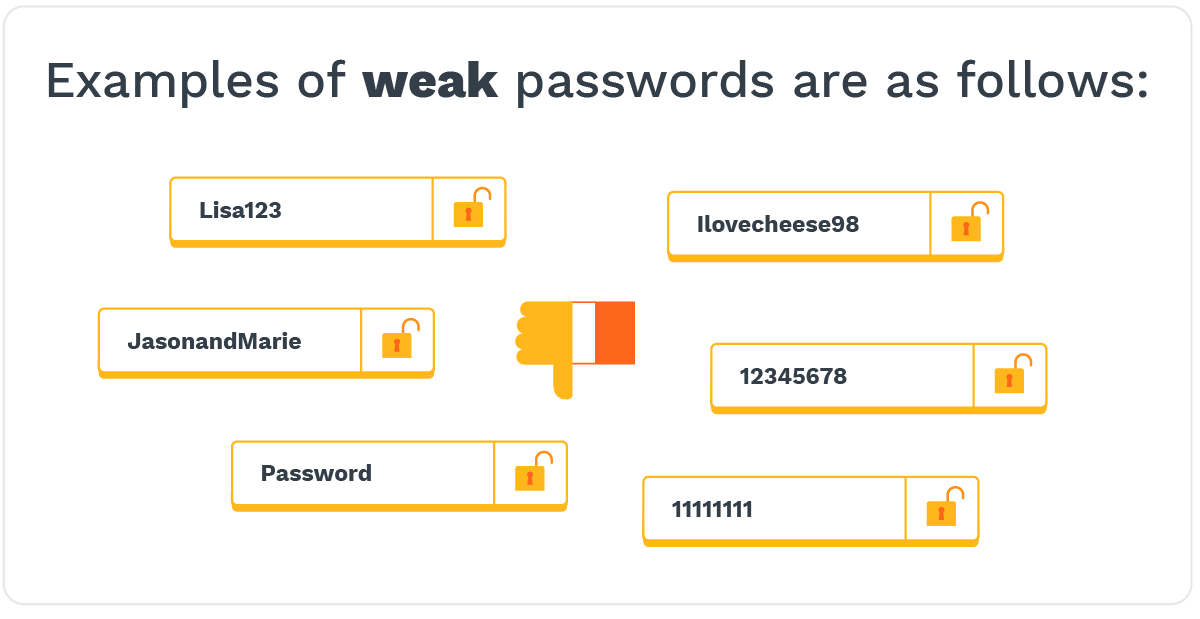
Weak Passwords: Despite the constant reminders, weak passwords remain a glaring issue. Reusing passwords across platforms, using easily guessable combinations, or failing to update them regularly can make a hacker's job significantly easier.
Misdelivery of Information: Sending sensitive information to the wrong recipients, either through email or other communication channels, can have dire repercussions. It could result in data leakage, compromising personal or corporate information.
Unpatched Systems: Neglecting to update software and applications can leave vulnerabilities unaddressed, giving hackers a clear pathway to exploit known weaknesses.

Social Engineering: Cyber attackers often exploit human psychology to gain unauthorized access. Manipulating trust, fear, or urgency, they trick individuals into revealing information or performing actions that compromise security.
Addressing Human Errors: A Multi-Faceted Approach
Education and Training: Raising awareness about cybersecurity risks and imparting knowledge about best practices is critical. Regular training sessions can help individuals recognize potential threats and react appropriately.
Strong Security Policies: Organizations should establish and enforce strict security policies, including password management, data sharing protocols, and guidelines for handling sensitive information.
Technology as a Safety Net: Implementing advanced cybersecurity tools such as intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and encryption mechanisms adds an additional layer of protection against human errors.
Constant Vigilance: Cyber threats evolve rapidly. Encouraging a culture of vigilance, where employees and individuals are encouraged to report suspicious activities, can help in early threat detection.
Encouraging Responsibility: Fostering a sense of personal responsibility for cybersecurity can make individuals more cautious and accountable for their online actions.
The Road Ahead
As technology continues to advance, the relationship between humans and the digital realm will only grow stronger. While we strive to achieve perfection in our digital defenses, it's crucial to remember that no system can be completely immune to human error. By acknowledging this reality and actively working to mitigate its effects, we can create a more secure digital landscape for ourselves and future generations.
In the end, the weakest link in cybersecurity is not the technology we rely on, but the human element that operates it. Through a combination of education, awareness, and a collective commitment to responsible digital behavior, we can strengthen this link and fortify our defenses against the ever-evolving threat of cyberattacks.
Mitigation Strategies:
Education and Training: A well-informed workforce is the first line of defense. Regular training sessions on cybersecurity best practices can equip employees with the knowledge they need to recognize and respond to potential threats.
Strict Access Control: Implement a principle of least privilege, allowing employees to access only the information necessary for their roles. This reduces the potential damage if an account is compromised.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring multiple forms of verification can significantly enhance security. Even if login credentials are compromised, an additional layer of authentication adds a crucial barrier for hackers.
Continuous Monitoring: Employ robust monitoring tools that can detect unusual activities in real-time. This helps identify potential breaches early, minimizing their impact.
Cultivate a Culture of Security: Foster an environment where cybersecurity is everyone's responsibility. Encourage open communication about potential threats and mistakes, without fear of retribution.
Conclusion:
As technology continues to evolve, the role of human error in cybersecurity remains a persistent challenge. While we can't eliminate human fallibility, we can certainly take proactive steps to minimize its impact. By combining technological measures with comprehensive education and a security-conscious culture, organizations and individuals can collectively work towards strengthening the weakest link in cybersecurity. Remember, the power to protect sensitive information ultimately rests in our own hands.