


Memory management keeps track of the status of each memory location, whether it is allocated or free. It allocates the memory dynamically to the programs at their request and frees it for reuse when it is no longer needed. Memory management meant to satisfy some requirements that we should keep in mind.
These Requirements of memory management are:
Relocation – The available memory is generally shared among a number of processes in a multiprogramming system, so it is not possible to know in advance which other programs will be resident in main memory at the time of execution of this program. Swapping the active processes in and out of the main memory enables the operating system to have a larger pool of ready-to-execute process.
When a program gets swapped out to a disk memory, then it is not always possible that when it is swapped back into main memory then it occupies the previous memory location, since the location may still be occupied by another process. We may need to relocate the process to a different area of memory. Thus there is a possibility that program may be moved in main memory due to swapping.
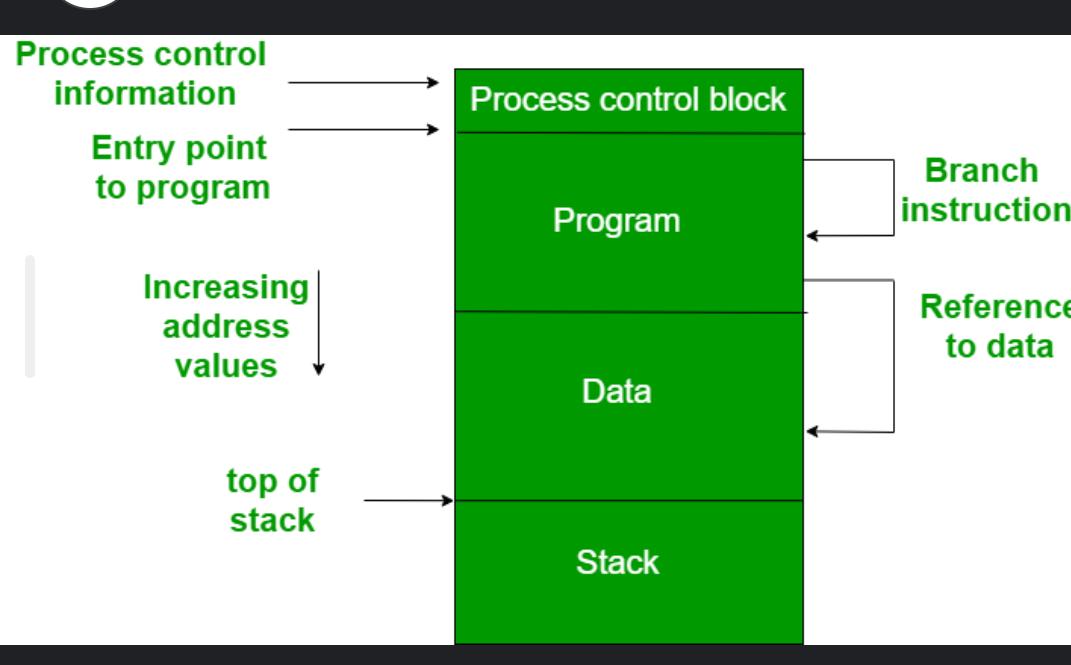
The figure depicts a process image. The process image is occupying a continuous region of main memory. The operating system will need to know many things including the location of process control information, the execution stack, and the code entry. Within a program, there are memory references in various instructions and these are called logical addresses.
After loading of the program into main memory, the processor and the operating system must be able to translate logical addresses into physical addresses. Branch instructions contain the address of the next instruction to be executed. Data reference instructions contain the address of byte or word of data referenced.
Protection – There is always a danger when we have multiple programs at the same time as one program may write to the address space of another program. So every process must be protected against unwanted interference when other process tries to write in a process whether accidental or incidental. Between relocation and protection requirement a trade-off occurs as the satisfaction of relocation requirement increases the difficulty of satisfying the protection requirement.
Prediction of the location of a program in main memory is not possible, that’s why it is impossible to check the absolute address at compile time to assure protection. Most of the programming language allows the dynamic calculation of address at run time. The memory protection requirement must be satisfied by the processor rather than the operating system because the operating system can hardly control a process when it occupies the processor. Thus it is possible to check the validity of memory references.
Sharing – A protection mechanism must have to allow several processes to access the same portion of main memory. Allowing each processes access to the same copy of the program rather than have their own separate copy has an advantage.
For example, multiple processes may use the same system file and it is natural to load one copy of the file in main memory and let it shared by those processes. It is the task of Memory management to allow controlled access to the shared areas of memory without compromising the protection. Mechanisms are used to support relocation supported sharing capabilities.
Logical organization – Main memory is organized as linear or it can be a one-dimensional address space which consists of a sequence of bytes or words. Most of the programs can be organized into modules, some of those are unmodifiable (read-only, execute only) and some of those contain data that can be modified. To effectively deal with a user program, the operating system and computer hardware must support a basic module to provide the required protection and sharing. It has the following advantages:
Modules are written and compiled independently and all the references from one module to another module are resolved by `the system at run time.
Different modules are provided with different degrees of protection.
There are mechanisms by which modules can be shared among processes. Sharing can be provided on a module level that lets the user specify the sharing that is desired.
Physical organization – The structure of computer memory has two levels referred to as main memory and secondary memory. Main memory is relatively very fast and costly as compared to the secondary memory. Main memory is volatile. Thus secondary memory is provided for storage of data on a long-term basis while the main memory holds currently used programs. The major system concern between main memory and secondary memory is the flow of information and it is impractical for programmers to understand this for two reasons:
The programmer may engage in a practice known as overlaying when the main memory available for a program and its data may be insufficient. It allows different modules to be assigned to the same region of memory. One disadvantage is that it is time-consuming for the programmer.
In a multiprogramming environment, the programmer does not know how much space will be available at the time of coding and where that space will be located inside the memory.
Hetvi parmar