


Concurrency in operating systems involves multiple processes or threads executing simultaneously, which can lead to complex interactions. Two common problems that arise in this context are deadlock and starvation. Here’s an overview of both:
1. *Deadlock*
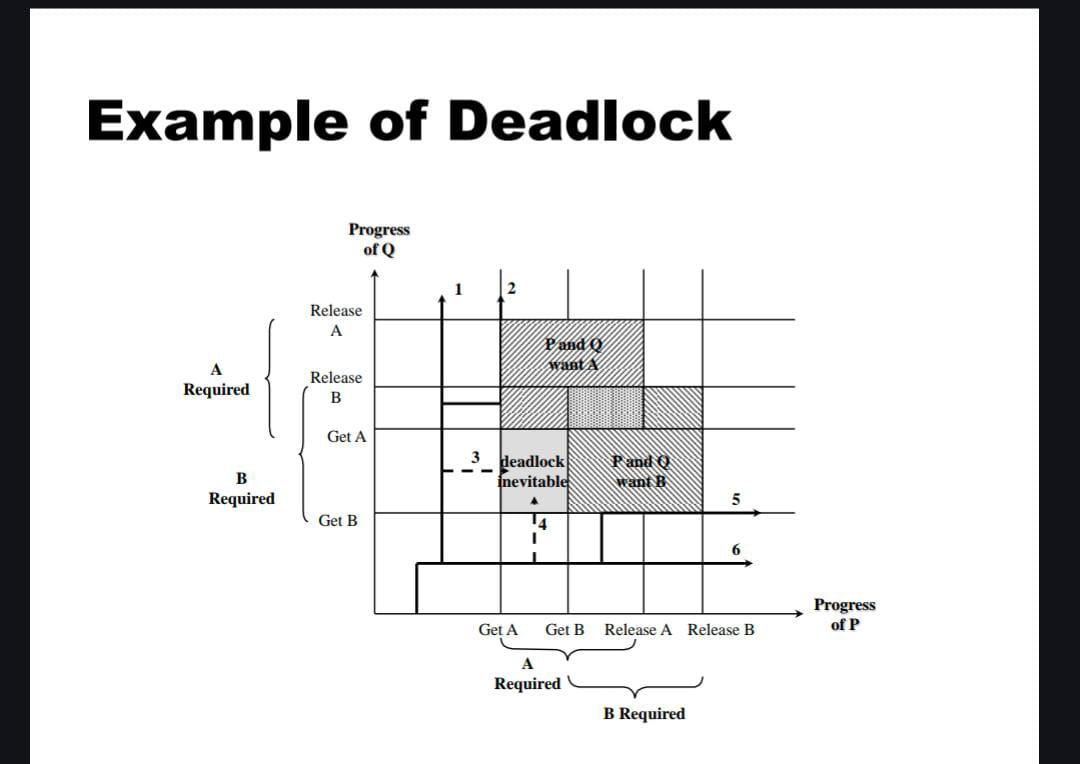
A deadlock occurs when a set of processes or threads become stuck in a situation where each one is waiting for a resource that the others in the set are holding. Since none of them can proceed, they remain in this waiting state indefinitely. Four conditions are necessary for a deadlock to occur:
- *Mutual Exclusion:* At least one resource must be held in a non-sharable mode; only one process can use the resource at any given time.
- *Hold and Wait:* A process holding at least one resource is waiting to acquire additional resources that are currently being held by other processes.
- *No Preemption:* Resources cannot be forcibly taken away from a process; they must be released voluntarily.
- *Circular Wait:* A closed chain of processes exists, where each process holds a resource that the next process in the chain is waiting for.
*Example:* Consider two processes, P1 and P2. P1 holds Resource A and is waiting for Resource B, while P2 holds Resource B and is waiting for Resource A. Neither process can proceed, leading to a deadlock.
*Deadlock Prevention and Avoidance*
- *Deadlock Prevention:* Modify one of the necessary conditions to ensure that a deadlock cannot occur (e.g., imposing a strict order on resource allocation to prevent circular wait).
- *Deadlock Avoidance:* Use algorithms (e.g., Banker's algorithm) to allocate resources in a way that ensures the system remains in a safe state.
2. *Starvation*
Starvation, also known as indefinite blocking, occurs when a process is perpetually denied necessary resources because other processes keep gaining access to them first. Unlike deadlock, where processes stop making progress due to being stuck in a cycle, starvation involves one or more processes making no progress because they are continually bypassed.
*Example:* Consider a scheduling system where high-priority processes keep getting resources, and a low-priority process is continually skipped over, leading to starvation.
*Solutions to Starvation*
- *Aging:* Gradually increase the priority of a waiting process over time to ensure it eventually gets the resources it needs.
- *Fair Scheduling Algorithms:* Use algorithms like round-robin or fair share that ensure all processes eventually receive attention.
Nikita Mitna
53003230109
Div-A